Background: Clinical factors including previous history of AF, heart failure, hypertension, valvular heart disease, increased age and male gender increase the risk of AF in CLL patients (Shanafelt, Leukemia and Lymphoma 2017). Treatment with Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKi) such as ibrutinib has also been associated with an increased risk of AF in CLL. We evaluated the role of artificial intelligence electrocardiography (AI-ECG) in predicting ibrutinib-induced AF (and, for reference, AF unrelated to ibrutinib) in patients with CLL.
Methods: We identified two cohorts of CLL patients using the Mayo Clinic CLL Database. Cohort 1 included patients evaluated within 12 months of CLL diagnosis who did not ever receive ibrutinib. Cohort 2 included patients who were treated with ibrutinib. The electrocardiographic signature of AF in sinus rhythm was detected by an AI-ECG algorithm previously developed using a convolutional neural network (Attia, Lancet 2019). The baseline AI-ECG AF score (positive defined as >0.10 on a scale of 0-1 which offers best balance between sensitivity and specificity per Attia et al.) was computed based on ECGs obtained within 10 years prior to CLL diagnosis (Cohort 1) or 10 years prior to initiation of ibrutinib therapy (Cohort 2). Patients with AF at baseline, missing data, or with ECGs previously used to train the AI algorithm were excluded. Reverse Kaplan Meier diagrams were plotted for both cohorts grouped by AI-ECG positivity. Cox proportional hazards were fitted to assess the predictive ability of AI-ECG in both cohorts.
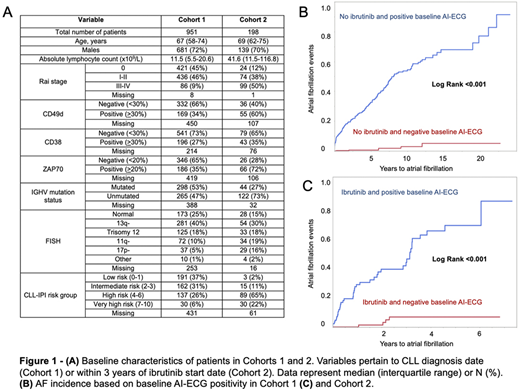
Results: After screening 2,739 patients and applying exclusion criteria (126 patients had baseline AF) a total of 1,149 patients with median 4 (interquartile range [IQR] 2-9) baseline ECGs were included in the analysis (Figure 1A). Cohort 1 included 951 patients with a median follow up of 3.0 (IQR 0.6-7.0) years and positive baseline AI-ECG in 546 (57%) patients. Cohort 2 included 198 patients with a median follow up of 1.6 (IQR 0.7-3.2) years and positive baseline AI-ECG in 91 (46%) patients. In Cohort 1, the median age was 67 years (IQR 58-72), 681 (72%) of patients were men, 68% had low/intermediate risk CLL-International Prognostic Index (IPI), and 32% had high/very high-risk CLL-IPI. In Cohort 2, the median age was 69 years (IQR 62-75), 139 (70%) of patients were men, 13% had low/intermediate risk CLL-IPI, and 87% had high/very high-risk CLL-IPI. AF occurred during follow up in 164 patients (17%) in Cohort 1 and 46 patients (23%) in Cohort 2. In both Cohorts 1 and 2, a positive baseline AI-ECG significantly increased the incidence of AF during follow up (log rank <0.001) (Figure 1B and C). Hazard ratios (for positive vs. negative AI-ECG) were 33.9 (95% confidence interval [CI] 15.0-76.6) for Cohort 1 and 14.8 (95% CI 5.3-41.3) for Cohort 2.
Conclusion: The addition of AI to a standard 12-lead ECG obtained during normal sinus rhythm - an inexpensive and ubiquitous test - predicts the occurrence of future AF in patients with CLL. This holds true irrespective of BTKi -based therapy and has important implications for the management of CLL patients.
Ding:Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; DTRM: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; alexion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kenderian:BMS: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Mettaforge: Patents & Royalties; Juno: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Lentigen: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Tolero: Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Humanigen: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Torque: Consultancy. Wang:Novartis: Research Funding; Innocare: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Kay:Juno Theraputics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cytomx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astra Zeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; MEI Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Kapoor:Cellectar: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding. Parikh:MorphoSys: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria; Verastem Oncology: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal